SERVICES
Energy desk officer service
Legal background for employing an energy specialist
The requirements for employing an energy specialist and their tasks are defined by the following regulations:
- 2015 Act LVII on Energy Efficiency
- Government Decree 122/2015 (V.26.) on the implementation of the Act on Energy Efficiency.
Employing an energy specialist has been mandatory since December 21, 2016.
Who is it applicable to?
A company is required to employ an energy specialist if, in the preceding 3 years, its average annual energy consumption exceeds:
- 400,000 kWh of electricity,
- 100,000 m³ of natural gas, or
- 3,400 GJ of heat.
Obligations of those required to employ an energy specialist
Companies whose energy consumption exceeds the limits specified in the previous point must employ at least one energy specialist who is independent of them in terms of labor law and company law, regardless of whether they are small, medium-sized or large companies.
The economic operator using the energy expert must inform the Office within 30 days of the date of appointment of the energy expert and of any changes in the data provided.
Tasks of the Energy Specialist
The energy specialist’s task is to promote an energy efficiency mindset and energy-efficient behavioral patterns within the company required to employ them. This involves:
- Participating as a professional observer and advisor in conducting regular energy audits, as well as in the development and monitoring of the energy management system in accordance with the EN ISO 50001 standard;
- Providing suggestions on energy-efficient operational solutions and energy efficiency development opportunities;
- Reporting on the energy savings achieved through implemented energy efficiency improvements and operational solutions;
- Preparing a monthly report for the company required to employ them, detailing the company's energy consumption for the current month and evaluating it against previous consumption data, investments, improvements, and other circumstances;
- Compiling an annual summary report by May 15 of the following year based on the monthly reports, outlining the energy savings achieved through implemented energy efficiency improvements and operational solutions. This report must be published on the company's website by May 31;
- Handling tasks related to energy procurement, energy security, and energy efficiency that fall within their scope.
Businesses that are required to use an energy specialist have additional obligations. These are set out in Decree 1/2020. (I. 16.) MEKH, which stipulates the following:
3. (1) In order to monitor electricity consumption, identify unjustified consumption and identify energy saving opportunities, economic operators required to employ an energy specialist shall install sub-meters at the following electricity consumption points if electricity consumption cannot be determined on the basis of installed capacity and operating time:
a) stand-alone electrical equipment with a rated power of more than 50 kW (in particular compressors, motors, pumps, other drives and technological equipment),
b) heat generators and air conditioning equipment with a rated electrical power of more than 70 kW.
(2) Monitoring the electricity consumption of economic operators required to use an energy specialist, identify unjustified consumption and identify energy saving opportunities, shall install submeters, disregarding equipment whose consumption is already measured by submeters specified in this Decree, and shall measure the maximum simultaneous power demand of equipment supplied through a single supply point and connected in a technological line (in particular: machines, machine lines, production lines, factory halls or buildings) where the maximum simultaneous power demand exceeds 100 kW.
(3) Equipment whose operating time does not exceed 1,000 operating hours per year on average over the three years preceding the reference year is exempt from the sub-metering requirement set out in paragraph (1).
Energy Audit
An energy audit is an examination based on measured data.
The purpose of an energy audit is to determine the energy sources used and their costs, to understand energy use, often to identify waste, and to explore and analyze more cost-effective ways of using energy, e.g., through the use of more advanced operating procedures or new equipment.
The energy audit report briefly summarizes the final results of the energy analysis, provides energy and cost saving recommendations, and, if necessary, includes a proposal for the bank.
Definition of Energy Auditing:
Energy auditing assesses the energy consumption across a facility and provides suggestions for reduction, supported by a full life-cycle cost analysis, an action plan, and, if needed, bank-ready proposals.

Goals of an Energy Audit/Assessment:
- Identifying the energy sources used and their costs
- Understanding energy usage patterns, including possible inefficiencies, and comparing specific values to similar facilities
- Analyzing and identifying cost-efficient energy usage methods, which may include:
- Advanced operational procedures
- New equipment
Economic evaluation of alternatives and defining applicable methods within a specific facility or industry
The Energy Audit Report includes:
- Results of the energy analysis
- Recommendations for energy and/or cost savings
- Bank-ready proposals if required
During an energy audit, the following areas are considered:
- Thermal energy (building systems and technology)
- Electrical energy (building electrical systems and technology)
Recommendations in the Audit:
- Low-cost measures with immediate or short payback times (under six months)
- Medium-cost measures (with a payback time of under three years)
- High-cost measures (with a payback time exceeding three years)
The energy certification of buildings will be part of the audit, as in many cases, the building itself is one of the main energy consumers. Upon request, we will examine the relevant funding opportunities and prepare the necessary materials for them.
Energy Auditing Process Steps:
Preparation:
Understanding the company's activities, services, and operations.
Collecting information by filling out data request forms.
Requesting available documents:
-
Documentation and technical descriptions of facilities,
-
Mechanical and electrical schematics,
-
Energy contracts and consumption data (water, gas, electricity, etc.),
-
Technical data and operating times of significant energy-consuming equipment,
-
Information on previous renovations and energy investments
Data Processing and Evaluation:
Assessing technical condition based on available documents and on-site inspections.
Proposing efficiency improvements, energy-saving technological changes, and considering renewable energy use; calculating the payback period of new equipment and technologies.
On-Site Inspections:
Conducting thorough on-site inspections if data provided is incomplete or insufficient
Results:
Based on the examination, the current condition of the inspected site and facilities will be presented, along with recommendations for more economical operation and/or management.
In addition to innovative solutions, other suggestions will be provided to reduce energy consumption and energy costs associated with traditional systems, either through minor investments or even without any investments.
Advantages of an Energy Audit:
-
Provides a complete overview of the organization’s energy consumption,
-
Offers actionable insights to enhance energy efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and lower associated costs,
-
Ensures compliance with energy efficiency legislation.
ISO 50001 – Energy Management System
The International Accreditation Forum (IAF) is responsible for issuing various international management systems. The ISO 50001:2018 standard, the Energy Management System standard, has been in force since February 21, 2020. ISO standards are becoming increasingly widespread, and customers may also require their suppliers to obtain various certifications. Furthermore, compliance with the ISO 50001 system can replace the energy audit obligation set out in the 2015 LVII Energy Efficiency Act. We provide our partners with support in implementing the ISO 50001 management system and maintaining the system.

We provide our partners with ISO 50001 management system implementation and system maintenance support. The system can take 3-12 months to set up. The audit consists of a 3-year cycle, with certification being obtained in the first year and surveillance audits ensuring that the certificate is maintained in the following years. The next 3-year cycle begins with a renewal audit.
ISO 50001 Audit Process
Preparation:
Understanding the company's activities, services, and operations.
Collecting information by filling out data request forms.
Requesting available documents:
- Documentation and technical descriptions of facilities,
- Mechanical and electrical schematics,
- Energy contracts and consumption data (water, gas, electricity, etc.),
- Technical data and operating times of significant energy-consuming equipment,
- Information on previous renovations and energy investments
On-Site Inspections:
Conducting thorough on-site inspections if data provided is incomplete or insufficient
Data Processing and Evaluation:
Assessing technical condition based on available documents and on-site inspections.
Proposing efficiency improvements, energy-saving technological changes, and considering renewable energy use; calculating the payback period of new equipment and technologies.
Results:
Based on the examination, the current condition of the inspected site and facilities will be presented, along with recommendations for more economical operation and/or management.
In addition to innovative solutions, other suggestions will be provided to reduce energy consumption and energy costs associated with traditional systems, either through minor investments or even without any investments.
Advantages of an Energy Audit:
-
Provides a complete overview of the organization’s energy consumption,
-
Offers actionable insights to enhance energy efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and lower associated costs,
-
Ensures compliance with energy efficiency legislation.
TAO – Corporate Tax Benefits for Energy Efficiency
Increasing energy efficiency has also been facilitated by tenders, subsidies and discounts. Act LXI of 1996 on corporate tax and dividend tax allows companies to reduce their corporate tax liabilities if they implement energy efficiency investments. The energy savings achieved must be at least 10%.
The amounts appearing as allowances in the TAO are determined on the basis of the investment costs as follows, but a maximum of EUR 30 million can be claimed.
The tax allowance is valid for 5+1 years, until the outstanding amount is exhausted.

The following types are distinguished:
- Tax allowance for investments/developments not related to buildings, determined as a percentage of the additional costs compared to a less energy-efficient solution. For example, 30% for large companies in Budapest and 65% for small companies in rural areas.
- In the absence of an alternative solution, determined as a percentage of the total investment cost. For example, 15% for large companies in Budapest and 42.5% for small companies in rural areas.
- Tax relief for investments in buildings is determined as a percentage of the total investment cost. Throughout Hungary, it is 10% for large companies, 20% for medium-sized companies, and 30% for small companies.
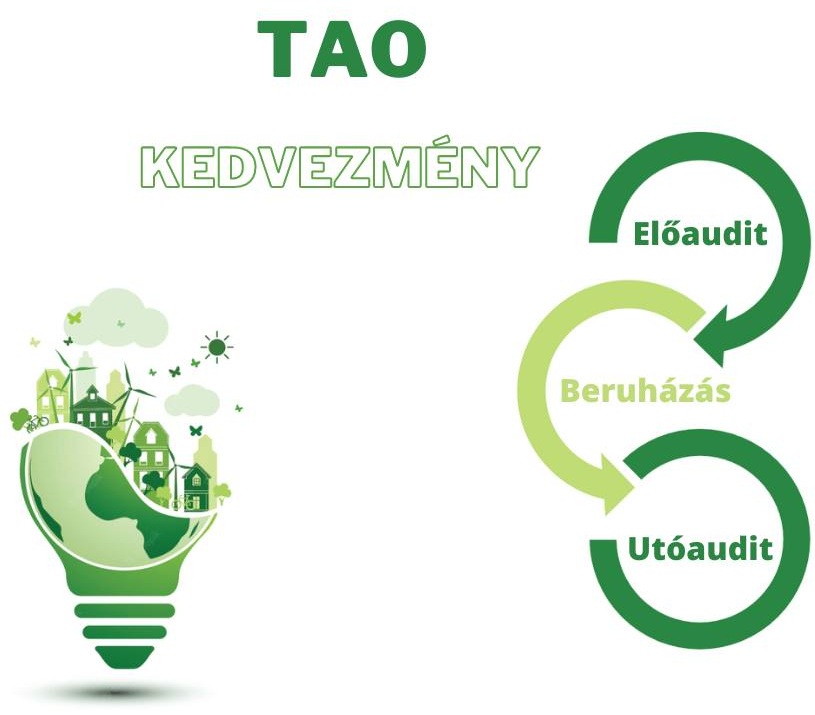
Procedure for claiming TAO relief:
- pre-investment energy efficiency audit carried out by an energy auditor listed in the MEKH register
-
implementation of the investment
-
post-investment energy efficiency audit and notification to the MEKH carried out by an energy auditor listed in the MEKH register.
The energy audit must be based on up-to-date, measured and traceable operational data relating to the energy consumption of the system under review and the load profiles. In the case of energy efficiency investments, only the component where the investment was made needs to be examined.
Benefits of TAO Energy Audit
- Offers actionable insights to enhance energy efficiency, reduce energy consumption, and lower associated costs,
-
Megfelel az energiahatékonysági törvényben és a társasági adóról és az osztalékadóról szóló törvényben foglaltaknak.
Energy Efficiency Obligation Scheme (EKR)
Purpose of EKR Introduction
Hungary has set the goal in the National Energy and Climate Plan that its final energy consumption in 2030 should not exceed the 2005 level of 785 PJ.
To achieve this, the following measures are necessary:
An annual energy savings rate of 0.8% and 7 PJ of new savings per year between 2021 and 2030.
EKR Overview
The obligated parties must introduce programs and implement measures that result in verified energy savings on the part of end users. The beneficiaries of the obligation system are domestic corporate and residential end users.

The entities responsible under the EKR include:
- Electricity traders
- Universal electricity suppliers
- Natural gas traders
- Universal gas suppliers
Fuel vendors selling to end-users for transportation purposes
Obligation Levels
Compared to previous years, the obligated party must achieve annual energy savings corresponding to a certain percentage of the amount of energy sold to end users in Hungary that is subject to the obligation.
The percentage is determined for each year, and the previous years to be taken into account, which has undergone several changes since the system was established.
Determining Energy Savings from Efficiency Measures
The obligated party must submit the necessary data to the Authority to calculate their annual energy savings obligation (per MEKH Decree 17/2020). Energy savings can be confirmed through an energy audit conducted by an accredited energy auditor or auditing organization.
Verification of Energy Savings
Az energiamegtakarítás megállapítása történhet energetikai auditor vagy energetikai auditáló szervezet által kiállított energetikai audit alapján (122/2015. (V. 26.) kormányrendelet)
Verification of Energy Savings
This is carried out by an energy auditing organization authorized to perform verification. Without this, the report cannot be submitted to the Office.
The energy auditing organization performing the verification is responsible for ensuring that the obligated party has taken into account the conversion factors, calculation methods and principles set out in Government Decree 122/2015. (V. 26.) on the implementation of the Energy Efficiency Act, and certifies the additional, significant contribution of the person implementing the investment or measure, as well as the amount of energy savings for the current year and subsequent years.
Meeting the Obligation
The obligated party can fulfill the energy savings requirement through energy efficiency investments or improvement measures within or outside its industry. Verified energy savings achieved by other obligated entities, non-obligated energy efficiency service providers, or third parties also count towards fulfilling the obligation.
Beneficiaries
Beneficiaries may include the obligated entity itself, its group members, clients, independent companies, or residential consumers. Supported by the obligated entity and external contributors, beneficiaries execute the project and achieve the savings. The auditor verifies the post-project savings.
EKR Project Flow and Monitoring

Monitoring Energy Efficiency Improvement Measures
If, during the verification, the Office finds that the reported energy savings or part thereof have not been determined correctly, it shall oblige the certifying body to make up for the amount of savings affected by the invalidation within 180 days, failing which it shall impose a fine of HUF 70,000 per 1 GJ of energy savings.
If the Office imposes a fine on the certification body four times within two years, the Office shall, in addition to imposing the fourth fine, prohibit the energy audit body from carrying out certification for a period of two years.
Energy Efficiency Contribution
Instead of fully meeting the energy savings requirement, an obligated party may choose to pay an energy efficiency contribution.
Compliance Verification and Penalties
The Authority monitors compliance with both the energy savings and contribution requirements. Failure to meet the obligation results in a 70,000 HUF fine per unmet 1 GJ/year energy savings.
EKR news
The EKR is currently the most dynamic system supporting energy efficiency improvements. The Energy Efficiency Act and the related implementing decree have been amended several times since the system was introduced. The list of eligible projects is changing.
Eligibility for the EKR requires prior substantial approval and an energy audit and/or certification prepared by an energy auditor listed in the MEKH register.
Engineering activities
Technical Preparation and Implementation
-
Professional Preparation
-
Engineering oversight
-
Technical supervision

Project management
Effective project management is crucial for the successful acquisition of awarded grant funding, which often involves extensive administrative tasks for applicants. Our project management experts develop comprehensive implementation plans, assisting partners from the project concept stage through to the end of the maintenance period. With a deep understanding of guidelines and documentation requirements set by the Coordinating Agency, we ensure timely submission of all necessary documents and reports, maximizing support and minimizing risks.
Our Project Management Services Include:
- Preparation and submission of payment request documents
- Project progress and status reports
- Project coordination
- Monitoring reports and progress updates
- Procurement coordination

Energy Grant Writing
Our experts help you determine the optimal technical solution and investment. We explore the characteristics of the given area and make recommendations for the use of renewable energies and the development of the appropriate combustion equipment and technologies. We perform cost analyses and prepare preliminary studies for larger investments.

We consider it important to find the optimal source of funding for our partners and to ensure the use of non-repayable grants through expert cooperation.
Our Grant Writing Services Include:
- Consultation
- Filling out application forms
- Form and content review of supporting documents
- Submission of grant applications
- Submission of additional required documents
- Signing grant agreements